What Do Squamous Metaplastic or Endocervical Cells on a Pap Smear Indicate?
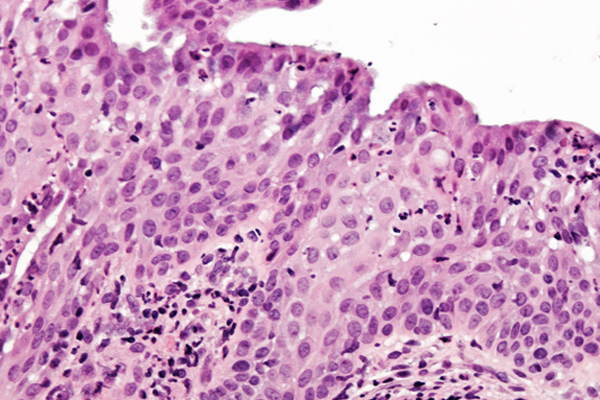
What are squamous metaplastic cells?
Squamous cells are types of cells found in various tissues throughout your body, including:
● your skin
● the outer surface of the cervix (ectocervix)
● the linings of your organs
When changes occur within these thin, flat-shaped cells, they may be described as metaplastic.
Squamous metaplasia is a noncancerous change in the cells that make up the tissue lining for organs and glands (epithelium). Most people have nonkeratinizing cervical squamous metaplasia. This condition doesn’t increase cancer risk. Keratinizing squamous metaplasia can turn into dysplasia, which may lead to cancer.
Squamous cells that may be precancerous or more likely to turn into cancer are described on a Pap test result as squamous intraepithelial lesions (SIL). These may be further classified as low-grade (LSIL) or high-grade (HSIL), indicating a low to high risk of cancer development.
If the pathologist finds
- Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US), this usually means that the pathologist has found irregular cells and could not determine why they were irregular. It can be due to other inflammatory or noncancerous changes of the cervix that will likely resolve on their own.
- Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) indicates lower-risk cervical cell change
- high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) cervical cell changes are present and may be at ahigher risk of turning into cancer
- atypical squamous cells (ASC-H) -changes were found within the squamous cells of your cervix, and you may also have HSIL
- atypical glandular cells (AGC) – changes within the glandular cells of the endocervix exhibit possible signs of precancer or cancer
- endocervical adenocarcinoma- indicates cancerous cells of the endocervix
- negative for intraepithelial lesions or malignancy (NILM)- no signs of malignancy or lesions were noted
- squamous metaplastic cells present- changes within cervical squamous cells were seen but without any concerning irregularities
- acute inflammation-this may indicate the presence infection and white blood cells in your sample
- atrophic changes- your cervix may be exhibiting signs of menopause
Takeaway
When it comes to reporting Pap smear test results, most medical professionals will either tell you that your results were standard or that you may need to undergo further testing to confirm possible irregularities.
It’s important to discuss any concerns about your Pap smear results with your doctor. Cervical cancer screenings are designed to detect possible precancer and cancerous cells for the earliest possible treatment.


