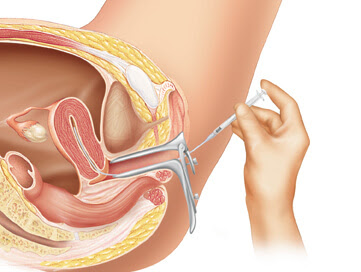
Intrauterine Insemination is a procedure for treating infertility. It is a type of artificial insemination where the sperms are placed in your uterus.
Before the placement, the sperms are washed and concentrated and are placed directly in your uterus around the time your ovaries releasing one or more eggs to be fertilized. The older types of artificial insemination placed the sperm in your vagina. Though this was easier, it was not as successful as the current methods.
When should IUI be used?
Low sperm count or decreased sperm mobility are the common reason for intrauterine insemination (IUI). However, IUI can also be selected for the treatment of the following conditions:
Donor Sperm: IUI is the commonly used method to achieve pregnancy for women who require the usage of donor sperm. Donor sperms are collected from the certified laboratory and thawed before the IUI procedure.
Unexplained Infertility: For unexplained infertility, IUI is the commonly performed first treatment along with ovulation medications.
Endometriosis-related infertility: For infertility related to endometriosis, good quality eggs are obtained using medications and IUI is performed as a first treatment.
Mild male factor infertility (subfertility): Semen analysis of your partner is one of the first steps of medical assessment of infertility. If the semen analysis shows low sperm count, abnormalities in shape and size of the sperms and weak sperm movement, IUI can be used to overcome these problems since preparing the sperms includes separating highly motile and normal sperms from the lower quality sperms.
Cervical Factor Infertility: Cervix is at the lower end of your uterus. It provides a hole between your uterus and vagina. Cervix secrets mucus during the time of ovulation. This mucus helps in the travel of sperms to the fallopian tubes from your vagina. If the cervical mucus is too thick, it will curb the journey of the sperms. IUI can be used to bypass the cervix and plant the sperm in your uterus directly. This will also increase the number of sperms available to meet the awaiting eggs.
Semen Allergy: There are some exceptional cases in which the woman could be allergic to her partner’s protein contents in his semen. Ejaculation of the semen into the vagina may cause redness, irritation, burning and swelling where it comes in contact with the skin. A condom can be used to protect yourself from the symptoms, but it will also prevent pregnancy. Hence, IUI can be used as an effective method to prevent allergies if they are severe. Since almost all of the semen proteins are removed before the sperm is deposited in the uterus.
Risks of Intrauterine Insemination:
Intrauterine Insemination is a simple and safer procedure. The risks of IUI are not severe and there is only a slight possibility of serious complications. The risk of IUI include:
Infection: As a result of the procedure, there may be a slight risk of developing an infection.
Spotting: There might be small vaginal bleeding due to the placement of the catheter in the uterus. But this bleeding does not have any effect on the chance of pregnancy.
Multiple Pregnancies: IUI is not directly associated with multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets or more). The risk of multiple pregnancies is slightly higher when coordinated with ovulation including medications. The risks of multiple pregnancies are slightly higher than a single pregnancy. The risks include early labour and low birth weight.
How to prepare yourself for the procedure?
IUI requires careful coordination before the actual procedure:
Preparing your semen: Your partner will need to provide a semen sample at the hospital or a vial of donor sperms which can be thawed and prepared. Sometimes the nonsperm elements in the semen may cause some allergic reactions in the woman’s body and may affect fertilization. Hence the sample will be wash to separate the highly active, normal sperms from the lower quality sperms and other elements present in the semen. The likelihood of pregnancy increases by using a small, highly concentrated sample of healthy normal sperms.
Monitoring for ovulation: The timing of intrauterine insemination is important. Therefore, monitoring for the signs of ovulation is critical. To do this, you can use an at-home ovulation predictor kit which detects the surge or release or increase of luteinizing hormone (LH) in your body. An imaging technique called transvaginal ultrasound can be used to visualize the ovaries and egg growth. You may also be given human chronic gonadotropin which will stimulations your ovulation and will make you ovulate one or more eggs at the correct time.
Determining the optimal time: Most time IUIs are done one or two days after the detection of ovulation. Your doctor should have planned out the timing of your IUI.
What to expect
The visit for the intrauterine insemination overall takes about 15 to 20 minutes and is normally done in the doctor’s office or clinic. The procedure of IUI takes about one or two minutes and is usually done by the doctor or a specially trained nurse.
During the procedure:
You will have to lie on the exam table and put your legs into stirrups. A speculum will be inserted into your vagina – similar to what you expect for a Pap test. During the procedure, a doctor or a nurse will
◆ Attach the vial containing the normal healthy sperm to one end of the catheter (long, thin, flexible tube)
◆ Inserts the catheter into your vagina, via cervical openings and into your uterus
◆ Empties the sperm sample into your uterus through the tube
◆ Removes the catheter and the speculum.
After the procedure:
After the procedure, you will be asked to lie on your back for a brief period. You can dress up and go on about your daily activities, once the procedure is done. You may encounter some spotting a day or two after the procedure.
Results:
You should wait for two weeks before taking the pregnancy test. Testing too soon might produce a result that is
False Negative: If pregnancy hormones are not at measurable levels, the test result may be negative, but you might be pregnant.
False Positive: If you were using ovulation-inducing medications like HCG, the medication which still circulates your system could indicate pregnancy, but you might not be pregnant.
Your doctor will advise you to return about two weeks after the home kit results for a blood test. The blood test will be more sensitive in detecting pregnancy hormones after fertilization.
If you do not get pregnant on the first try of IUI, you can try it again before moving on to other fertility treatments. Moreover, the same therapy performed continuously for three to six months will maximize your chances of pregnancy.
Success rates of IUI
The success of IUI depends on several factors. If a couple has the IUI procedure done every month, the success rates may increase to up to 20% each cycle depending on variables such as female age, the reason for infertility and whether fertility drugs were used.Though IUI is a less expensive and less invasive option. The pregnancy rates from IUI are lower than IVF. If you are interested in IUI, you might want to talk to a doctor.


